Statistics & Evidence Based Healthcare
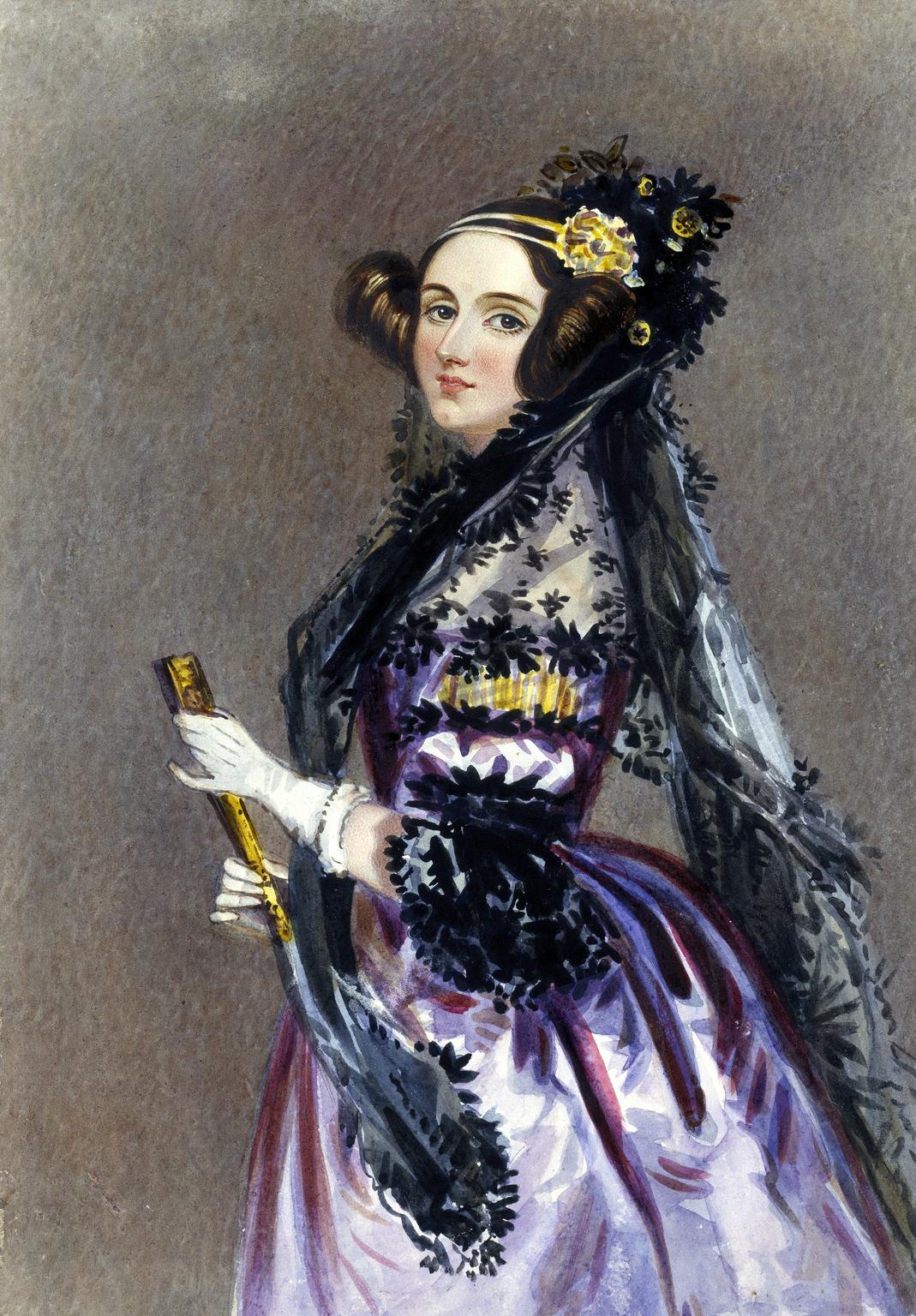
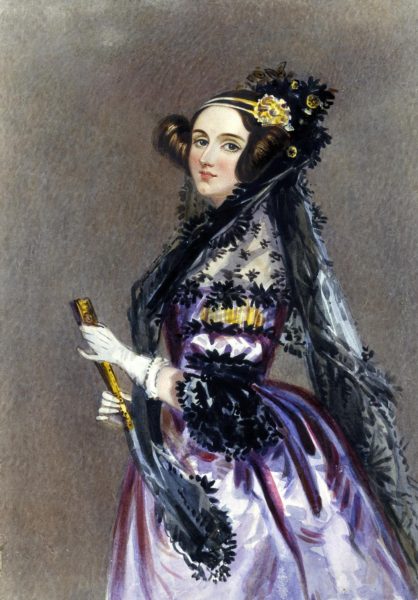
Ada Lovelace, 1815-1852
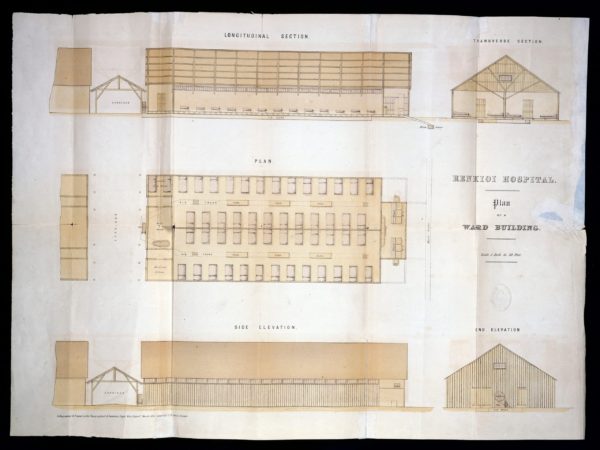
Display No. 41
Ada Lovelace was an English mathematician and friend to Florence Nightingale. Lovelace worked with Charles Babbage on the ‘Analytical Engine’, a calculation machine which is regarded by many as an early version of the computer. She wrote the world’s first machine algorithm is regarded as the world’s first computer programmer. When Lovelace published her work, she described her vision for the future of computing. She predicted that computers could be used to compose music and create graphics. She hoped her work would make it easier for researchers to process their data, and encourage the pursuit of evidence-based practice.
Exhibits from ‘Statistician & Evidence Based Healthcare’
Discover the 200 Exhibits
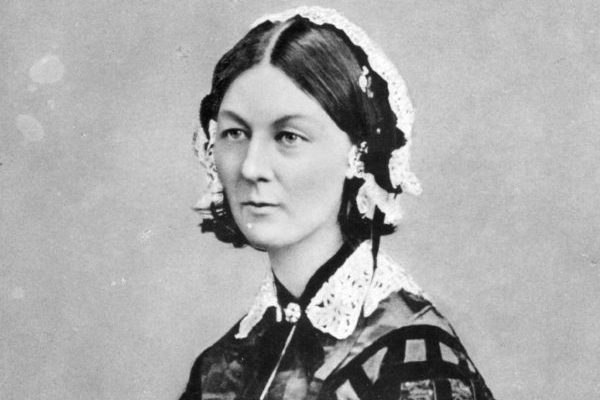
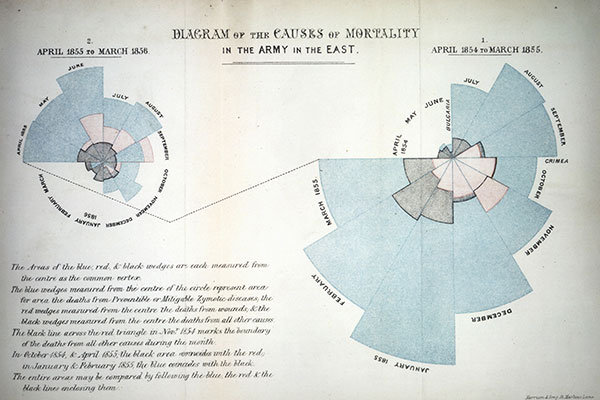
Nightingale is respected worldwide for her pioneering role in developing the nursing profession, her statistical work, and her evidence-based approach to healthcare. In honour of her bicentenary the World Health Organisation have named 2020 the Year of the Nurse and Midwife.
In our special exhibition, you will find out about objects, people and places which tell interesting stories about Florence’s life and legacy. You’ll discover artefacts from her life, people she both inspired and challenged, and places she helped to shape. There’s many more insights too!
Please click on the different sections of her famous coxcomb diagram to explore various aspects of her life and legacy. We hope you enjoy exploring!